To calculate Hooke Law:
-
What you want to calculate
-
Spring Force Constant(k)
N/m
-
Distance from Equilibrium(x)
m
-
Spring Equilibrium Position(x0)
m
-
Force(Fx)
N
-
Formula:
Force:
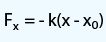
Spring Force Constant:

Distance from Equilibrium:

Spring Equilibrium Position:
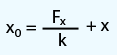
where,
F
x = Force,
k = Spring Force Constant,
x =Distance from Equilibrium,
x
0 = Spring Equilibrium Position.
In short Hooke's law can be explained as " F = kx" and to explain it further Hooke’s law states that force need to compress or extend a spring is directly proportional to the distance covered and constant factor i.e. stiffness is considered during this calculation.
Know more -
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hooke's_law

